目录
深入理解AOP:8大核心概念详解与代码实践
什么是AOP?
AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming,面向切面编程)是一种编程范式,旨在通过将横切关注点(如日志记录、事务管理等)与业务逻辑分离来提高代码的模块化。AOP允许开发者将分散在应用程序各处的通用功能集中管理,从而减少代码重复,提高可维护性。
AOP的8大核心概念
1. 切面(Aspect)
切面是模块化横切关注点的类。它包含通知(Advice)和切点(Pointcut)。
java@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
// 前置通知
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void logBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("准备执行: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
// 后置通知
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))",
returning = "result")
public void logAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
System.out.println("方法执行完成: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName()
+ " 返回结果: " + result);
}
}
2. 连接点(Join Point)
连接点是程序执行过程中的一个点,如方法调用、异常抛出等。在Spring AOP中,连接点总是表示方法执行。
java@Before("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void logJoinPoint(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
// 获取连接点信息
System.out.println("目标方法: " + joinPoint.getSignature().toLongString());
System.out.println("参数: " + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
System.out.println("目标对象: " + joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName());
System.out.println("代理对象: " + joinPoint.getThis().getClass().getName());
}
3. 通知(Advice)
通知是切面在特定连接点执行的动作。Spring AOP支持5种通知类型:
java@Aspect
@Component
public class AdviceTypesAspect {
// 1. 前置通知 - 在方法执行前执行
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void beforeAdvice() {
System.out.println("前置通知执行");
}
// 2. 后置通知 - 在方法正常完成后执行
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))",
returning = "result")
public void afterReturningAdvice(Object result) {
System.out.println("后置通知执行,返回值: " + result);
}
// 3. 异常通知 - 在方法抛出异常时执行
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))",
throwing = "ex")
public void afterThrowingAdvice(Exception ex) {
System.out.println("异常通知执行,异常: " + ex.getMessage());
}
// 4. 最终通知 - 在方法执行后执行(无论是否抛出异常)
@After("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void afterAdvice() {
System.out.println("最终通知执行");
}
// 5. 环绕通知 - 在方法调用前后执行自定义行为
@Around("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public Object aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕通知 - 方法执行前");
Object result = joinPoint.proceed(); // 执行目标方法
System.out.println("环绕通知 - 方法执行后");
return result;
}
}
4. 切点(Pointcut)
切点是一个表达式,用于匹配连接点。Spring使用AspectJ的切点表达式语言。
java@Aspect
@Component
public class PointcutExamplesAspect {
// 匹配com.example.service包下所有类的所有方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void serviceLayer() {}
// 匹配所有get开头的方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service.*.get*(..))")
public void getterMethods() {}
// 匹配所有public方法
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void publicMethods() {}
// 组合切点
@Pointcut("serviceLayer() && getterMethods()")
public void publicGetterMethods() {}
// 使用切点
@Before("publicGetterMethods()")
public void logPublicGetter() {
System.out.println("执行public getter方法");
}
}
5. 引入(Introduction)
引入允许我们向现有类添加新方法或属性。
javapublic interface Auditable {
void setLastModified(Date date);
Date getLastModified();
}
@Aspect
@Component
public class AuditableIntroductionAspect {
@DeclareParents(value = "com.example.service.*",
defaultImpl = AuditableImpl.class)
public static Auditable auditable;
}
public class AuditableImpl implements Auditable {
private Date lastModified;
@Override
public void setLastModified(Date date) {
this.lastModified = date;
}
@Override
public Date getLastModified() {
return lastModified;
}
}
// 使用
@Service
public class UserService {
// 原本没有Auditable接口的方法
}
// 现在可以这样使用
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
public void testIntroduction() {
((Auditable)userService).setLastModified(new Date());
System.out.println(((Auditable)userService).getLastModified());
}
6. 目标对象(Target Object)
目标对象是被一个或多个切面通知的对象。
java@Service
public class UserService {
public String getUserById(Long id) {
return "User " + id;
}
}
@Aspect
@Component
public class TargetObjectAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.UserService.*(..))")
public void beforeUserServiceMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
// 获取目标对象
Object target = joinPoint.getTarget();
System.out.println("目标对象: " + target.getClass().getName());
}
}
7. AOP代理(AOP Proxy)
AOP框架使用代理模式来创建代理对象,以实现切面功能。
java@Service
public class OrderService {
public String createOrder(String orderDetails) {
return "Order created: " + orderDetails;
}
}
@Aspect
@Component
public class ProxyAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.example.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public Object aroundOrderService(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("代理对象: " + joinPoint.getThis().getClass().getName());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
// 测试
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
public void testAopProxy() {
System.out.println("注入的OrderService类型: " + orderService.getClass().getName());
// 输出可能是: com.example.service.OrderService$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$...
}
8. 织入(Weaving)
织入是将切面应用到目标对象以创建代理对象的过程。Spring AOP在运行时进行织入。
java// 展示织入效果的示例
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy // 启用AspectJ自动代理(织入)
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public LoggingAspect loggingAspect() {
return new LoggingAspect();
}
@Bean
public UserService userService() {
return new UserService();
}
}
// 测试织入
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);
userService.getUserById(1L);
context.close();
}
完整示例:实现日志记录和性能监控
java@Aspect
@Component
public class ComprehensiveAspect {
// 定义切点
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service..*(..))")
public void serviceMethods() {}
// 方法执行前记录日志
@Before("serviceMethods()")
public void logMethodStart(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().toShortString();
System.out.println("[日志] 开始执行: " + methodName);
System.out.println("[日志] 参数: " + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
// 方法执行后记录日志
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "serviceMethods()", returning = "result")
public void logMethodSuccess(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().toShortString();
System.out.println("[日志] 执行成功: " + methodName);
System.out.println("[日志] 返回值: " + result);
}
// 方法抛出异常时记录日志
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "serviceMethods()", throwing = "ex")
public void logMethodException(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception ex) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().toShortString();
System.out.println("[日志] 执行异常: " + methodName);
System.out.println("[日志] 异常信息: " + ex.getMessage());
}
// 方法执行后记录完成日志(无论成功或失败)
@After("serviceMethods()")
public void logMethodEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().toShortString();
System.out.println("[日志] 执行结束: " + methodName);
}
// 性能监控
@Around("serviceMethods()")
public Object monitorPerformance(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().toShortString();
try {
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
long executionTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
System.out.println("[性能] " + methodName + " 执行时间: " + executionTime + "ms");
return result;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
long executionTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
System.out.println("[性能] " + methodName + " 执行失败时间: " + executionTime + "ms");
throw ex;
}
}
// 引入新功能
@DeclareParents(value = "com.example.service.*",
defaultImpl = VersionableImpl.class)
public static Versionable versionable;
}
public interface Versionable {
void setVersion(String version);
String getVersion();
}
public class VersionableImpl implements Versionable {
private String version = "1.0";
@Override
public void setVersion(String version) {
this.version = version;
}
@Override
public String getVersion() {
return version;
}
}
// 业务服务类
@Service
public class ProductService {
public String getProductInfo(Long productId) {
// 模拟业务逻辑
if (productId == 1L) {
return "iPhone 13";
} else if (productId == 2L) {
return "MacBook Pro";
}
throw new RuntimeException("产品不存在");
}
}
// 测试类
@SpringBootTest
public class AopTest {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
@Test
public void testAopFeatures() {
// 测试正常流程
System.out.println("测试正常流程:");
String product = productService.getProductInfo(1L);
System.out.println("获取产品: " + product);
// 测试异常流程
System.out.println("\n测试异常流程:");
try {
productService.getProductInfo(999L);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("捕获异常: " + e.getMessage());
}
// 测试引入的功能
System.out.println("\n测试引入功能:");
Versionable versionable = (Versionable) productService;
System.out.println("当前版本: " + versionable.getVersion());
versionable.setVersion("2.0");
System.out.println("更新后版本: " + versionable.getVersion());
}
}
AOP最佳实践
- 合理使用通知类型:
- 使用
@Around实现复杂逻辑(如重试机制) - 使用
@AfterReturning处理正常返回结果 - 使用
@AfterThrowing处理异常情况 - 使用
@Before进行简单的预处理
- 切点表达式优化:
- 避免过于宽泛的切点表达式
- 使用
@Pointcut定义可重用的切点 - 组合多个切点表达式提高精确度
- 性能考虑:
- 避免在切面中执行耗时操作
- 对于高频调用的方法,尽量减少切面逻辑
- 考虑使用条件判断减少不必要的切面执行
- 异常处理:
- 在
@Around通知中正确处理异常 - 不要吞没业务异常(除非明确需要)
- 记录足够的异常上下文信息
- 日志记录:
- 记录有意义的上下文信息
- 控制日志级别,避免产生过多日志
- 考虑使用MDC(Mapped Diagnostic Context)记录跟踪信息
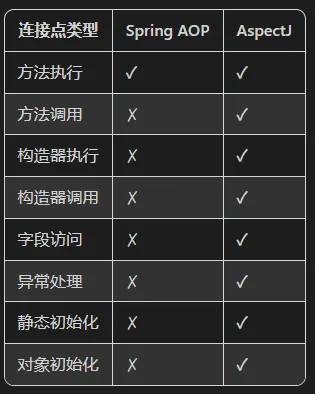
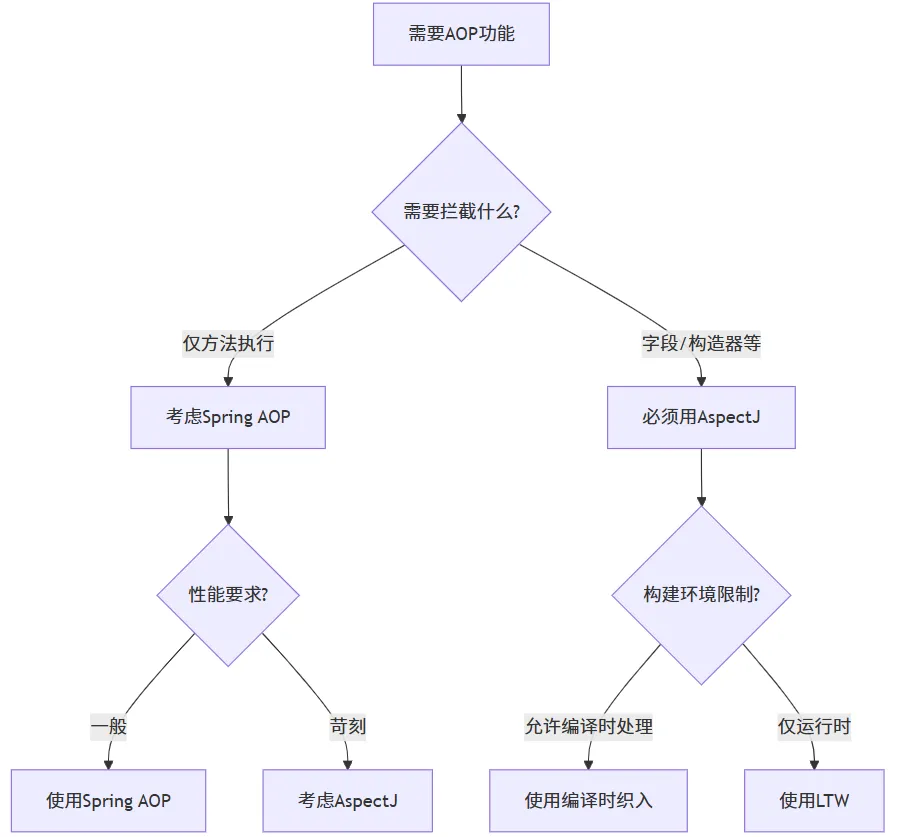
Spring AOP和原生AspectJ对比
总结
AOP是Spring框架的核心功能之一,通过将横切关注点与业务逻辑分离,可以显著提高代码的可维护性和可重用性。理解AOP的8大核心概念(切面、连接点、通知、切点、引入、目标对象、AOP代理和织入)是掌握AOP编程的基础。在实际项目中,合理使用AOP可以优雅地解决日志记录、事务管理、安全控制、性能监控等共性问题,让开发者能够更专注于业务逻辑的实现。
通过本文的代码示例,你应该已经对如何在Spring中实现AOP有了全面的了解。建议在实际项目中从小规模开始应用AOP,逐步积累经验,最终达到熟练运用的程度。
本文作者:JACK WEI
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录